Effect undetermined transquântico graceli.
Physical processes and laser photon radiation, laser effect on plates of metals and radiation from these phenomena.
Where we have a indeterminalidade and transquântica relativity with ejections and transpassagens laser and x-ray range. And physical alternations and internal and external.
See effect graceli laser photons - the laser action, produces photons and other internal and external changes, i.e., the already known photoelectric effect have actions on external radiation, but not in the interactions, the conductivity rearrangements loads, symmetries, parities etc. where we have a greater or lesser indeterminalidade as actions on these plates and the gas space. which modifies isotopes and decay of radioactivities, mergers and fissions.
In other words, what we have are internal and external changes and variations by external actions, modifying the stability of the internal phenomena to produce external.
That is, the external stimuli radiation depends on the internal phenomena such as shift of electrons, thermal, weights, spin variation of angular momentum, inertial internal flows interactions accelerated conductivity, etc.
However these phenomena follows a growing instability increases as the time process on plates, and on isotopes or even radioactive as uranium and thorium, leading to a indeterminalidade graceli intensity, scope, and direction and transformations.
EtqG = Ee = i + vi = Fe = IIIG.
EtqG = Ee = i + vi = Fe = IIIG. = Effect transquântico graceli = External stimuli = internal stimuli internal variation = + = internal phenomena instability, unpredictability and indeterminalidade graceli.
Graceli effect and electro magnetic.
These variations happen with magnetic and electric or external stimuli, but with higher intensities.
The concave and convex nature of the scattering of light, and electric fields.
The light scattering because what we mean curve deformation. That is, the light is dispersion, opening just behind objects and stars will have the light reflecting on the other hand, since it passes the sides continues its dispersion. This we see also in the water. In other words, what we have is the scattering of light and not its curving. For if this were bowing bowing would only be concave with respect to gravitational masses, but what happens dispersions are both concave as convex.
That is, the light itself has the characteristic of being next curve when bodies and means. This is independent of gravitational field.
We see this in the water, and you can see it when they are ejected beams of light behind objects and bodies, we see that it will appear on both sides ,, ie they dispersed independent mass bodies, media, or field gravity, i.e., the curvature is a light characteristics over itself, this also see the electrical lightning space toward the earth.
Or even see in the refrigerator magnetism when we put planks and intermediate plates between the magnet and metals.
That is, what we have is the scattering phenomenon which produces the convex and concave phenomenon at the same time. That is, if the gravity encurvaria space changing orbits and producing the translational light would only be concave relative to the star which produces the field, but not so much light is concave as convex.
It is possible to measure the degree of curvature having the concave as convex, meaning the dispersion by the action of interactions between photons and electrons.
Efeito transquântico indeterminado Graceli.
Física de processos de laser e radiações fótons, efeito de laser sobre placas de metais e radiações a partir destes fenômenos.
Onde temos um indeterminalidade e relatividade transquântica com ejeções e transpassagens por laser e raios x e gama. E alternações físicas e internas e externas.
Ver efeito laser de fótons Graceli - a ação de laser, fótons e outros produz variações interna e externa, ou seja, o efeito fotoelétrico já conhecido tem ações na radiação externa, mas não nas interações, nas condutividade, reordenamentos de cargas, simetrias, paridades, etc. onde passamos a ter uma indeterminalidade maior ou menor conforme ações destes sobre placas e gases no espaço. onde modifica isótopos e decaimentos de radioatividades, fusões e fissões.
Ou seja, o que temos são alterações e variações interna e externa por ações externa, modificando a estabilidade dos fenômenos interno para produzir os externos.
Ou seja, a radiação externa depende de estímulos sobre os fenômenos interno, como deslocamento de elétrons, térmicas, de cargas, de variação de spin, momentum angular, inércia de fluxos interno, interações , condutividade acelerada, etc.
Porem estes fenômenos segue uma instabilidade crescente conforme aumenta o tempo de processo sobre chapas, e sobre isótopos ou mesmo dos radioativos como urânio e tório, levando a uma indeterminalidade Graceli de intensidade, alcance, e direção e transformações.
Φ = tG
tG=EtqG 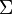
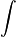 I = EtqG =Ee = ei + vi = Fe = iiiG.
I = EtqG =Ee = ei + vi = Fe = iiiG.
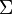
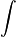 I = EtqG =Ee = ei + vi = Fe = iiiG.
I = EtqG =Ee = ei + vi = Fe = iiiG.
iiiG = INDETERMINISMO GRACELI.
Ra rmm = mec+ in.
Rotation of the star + rotation of the magnetic mass = energy Massa conquered + momentary energy.
EtqG =Ee = ei + vi = Fe = iiiG.
EtqG =Ee = ei + vi = Fe = iiiG. = Efeito transquântico graceli = Estímulos externos = estímulos interno + variação interna = fenômenos interno = instabilidades, imprevisibilidade e indeterminalidade Graceli.
Efeito Graceli eletro e magnético.
Estas variações acontecem com estímulos externo magnético e ou elétrico, mas com intensidades maiores.
A natureza côncava e convexa da dispersão da luz, campos e eletricidade.
A dispersão de luz causa o que entendemos de deformação curva. Ou seja, a luz se encontra em dispersão, se abrindo, mesmo atrás de objetos e astros teremos a luz refletindo do outro lado, pois a que passa pelos lados continua a sua dispersão. Isto vemos também dentro da água. Ou seja, o que temos é a dispersão da luz e não o seu encurvamento. Pois, se houvesse encurvamento este encurvamento seria só côncavo em relação a massas gravitacionais, mas o que ocorre são dispersões tanto côncava quanto convexa.
Ou seja, a própria luz tem a característica de ser curva quando próxima de corpos e meios. Isso independe de campo gravitacional.
Vemos isto dentro da água, e se pode ver isto quando são ejetados feixes de luz atrás de objetos e corpos, veremos que ela vai aparecer dos dois lados,, ou seja, elas se dispersa independente de massa, corpos, meios, ou de campo gravitacional, ou seja, a curvatura é uma características da luz sobre ela mesma, isto também vemos na eletricidade de relâmpagos no espaço em direção a terra.
Ou mesmo vemos no magnetismo de imas quando colocamos pranchas e placas intermediárias entre o ima e metais.
Ou seja, o que temos é o fenômeno da dispersão que produz o fenômeno côncavo e convexo ao mesmo tempo. Ou seja, se fosse a gravidade que encurvaria o espaço alterando as órbitas e produzindo a translação a luz seria apenas côncava em relação ao astro que produz o campo, mas não a luz é tanto côncava quanto convexa.
E é possível medir o grau de curvatura tendo do côncavo quanto do convexo, ou seja, da dispersão pela ação de interações entre os fótons e elétrons.